4. Creating components
With two pages comprised entirely of Carbon components, let’s revisit the landing page and build a couple components of our own by using Carbon icons and tokens.
- Fork, clone and branch
- Review design
- Create components
- Use components
- Add styling
- Check accessibility
- Submit pull request
Preview
Carbon provides a solid foundation for building web applications through its color palette, layout, spacing, type, as well as common building blocks in the form of components. So far, we’ve only used Carbon components to build out two pages.
Next, we’re going to use Carbon assets to build application-specific components. We’ll do so by including accessibility and responsive considerations all throughout.
A preview of what you’ll build (see bottom of page):
Fork, clone and branch
This tutorial has an accompanying GitHub repository called carbon-tutorial that we’ll use as a starting point for each step. If you haven’t forked and cloned that repository yet, and haven’t added the upstream remote, go ahead and do so by following the step 1 instructions.
Branch
With your repository all set up, let’s check out the branch for this tutorial step’s starting point.
git fetch upstreamgit checkout -b vue-step-4 upstream/vue-step-4
Build and start app
Install the app’s dependencies (in case you’re starting fresh in your current directory and not continuing from the previous step):
yarn
Then, start the app:
yarn serve
You should see something similar to where the previous step left off.
Review design
Here’s what we’re building – an informational section that has a heading and three subheadings. Each subheading has accompanying copy and a pictogram. We’ll assume that this informational section is used elsewhere on the site, meaning it’s a great opportunity to build it as a reusable component. As for naming, we’ll call it an
InfoSection
InfoCard
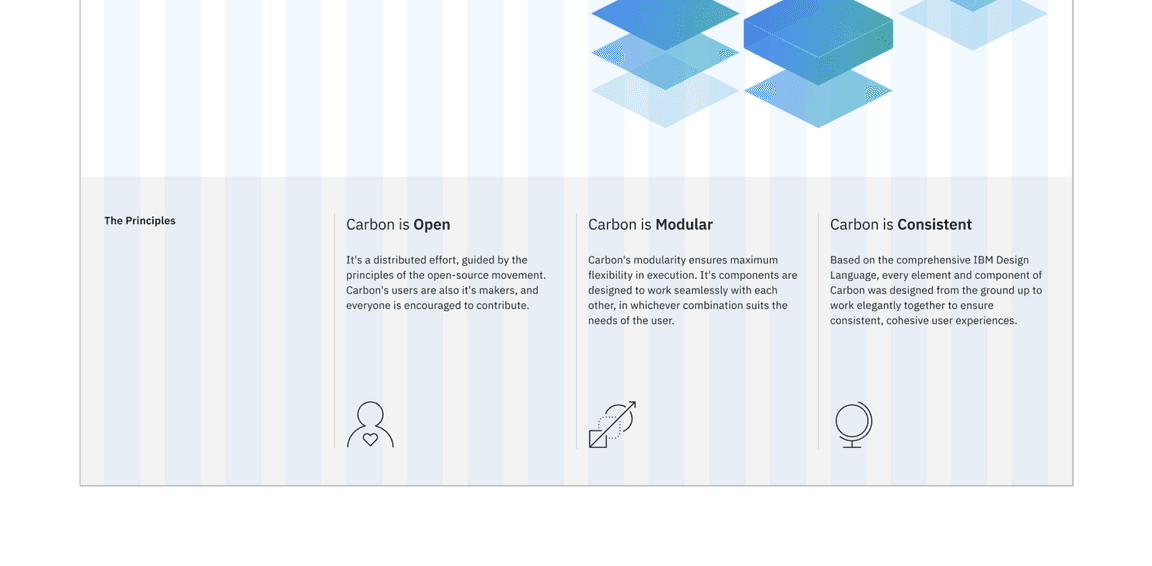
Info section layout
Create components
First we need files for the components, so create an
InfoSection
src/components
Info
Add files
src/components/InfoSection├──index.js└──InfoCard.vue└──InfoSection.vue
Like our other components,
index.js
import InfoSection from './InfoSection';import InfoCard from './InfoCard';export { InfoSection, InfoCard };
InfoSection component
Let’s create the parent component that includes the “The Principles” heading. That markup currently looks like this in
LandingPage.vue
<div class="cds--row landing-page__r3"><div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4"><h3 class="landing-page__label">The Principles</h3></div><div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4">Carbon is Open</div><div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4">Carbon is Modular</div><div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4">Carbon is Consistent</div></div>
We want to do a few things when abstracting it to a component. First, we only want Carbon (
cds--
landing-page__r3
We’ll also:
- Add component class names like andinfo-sectioninfo-section__heading
- Semantically use instead of<section><div>
- Update the grid columns to match the design
- Replace withThe Principles{{heading}}
- Replace columns 2 - 4 with a slot.
Using
props
InfoCard
<template><section class="cds--row info-section"><div class="cds--col-md-8 cds--col-lg-4 cds--col-xlg-3"><h3 class="info-section__heading">{{ heading }}</h3></div><slot /></section></template>
Then name our component and add a property to the script section.
<script>export default {name: "InfoSection",props: {heading: String}};</script>
At this point let’s add styling for the new class names that we just added.
<style lang="scss">@import "../../styles/_carbon-utils";.info-section__heading {@include type-style('heading-01');}</style>
InfoCard component
Next up we’re going to build a component for columns 2 - 4, which currently looks like
<div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4">Carbon is Open</div>
<template><articleclass="info-card cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4 cds--col-xlg-3 cds--offset-xlg-1"><h4 class="info-card__heading">{{ heading }}</h4><p class="info-card__body">{{ body }}</p><component :is="icon" /></article></template>
Give it a name and add props
<script>export default {name: "InfoCard",props: {heading: String,body: String,icon: Object}};
In doing so, we:
- Used the semantic instead of<article><div>
- Added classesinfo-card
- Used to render the heading, body copy, and iconprops
- Set columns to match the grid
Use components
Our styling is not complete yet, but with our components built let’s put them to use. In
LandingPage.vue
<script>import { InfoSection, InfoCard } from '../../components/InfoSection';export default {name: 'LandingPage',components: { InfoSection, InfoCard }};</script>
While we’re here next to the component imports, let’s import the icons that we’ll need as well.
import { Globe32, PersonFavorite32, Application32 } from '@carbon/icons-vue';
Don’t forget to add the icons to the list of components used in our template. Wait a minute, are they being used by our template? Well, yes and no. The components are going to be passed as an attribute rather than being used as a DOM element. Vue treats this use case differently and instead of adding to the components property, we need to assign the icons directly to the
this
In the script section of the component add the lifecycle method
created()
created() {// Add icons to thisObject.assign(this, {Globe32,PersonFavorite32,Application32});}
With everything imported, replace the current template content:
<div class="cds--row landing-page__r3"><div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4"><h3 class="landing-page__label">The Principles</h3></div><div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4">Carbon is Open</div><div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4">Carbon is Modular</div><div class="cds--col-md-4 cds--col-lg-4">Carbon is Consistent</div></div>
With the new components:
<info-section heading="The Principles" class="landing-page__r3"></info-section>
Then slot the
InfoCard
InfoSection
<info-section heading="The Principles" class="landing-page__r3"><info-cardheading="Carbon is Open"body="It's a distributed effort, guided by the principles of the open-source movement. Carbon's users are also it's makers, and everyone is encouraged to contribute.":icon="PersonFavorite32"/><info-cardheading="Carbon is Modular"body="Carbon's modularity ensures maximum flexibility in execution. It's components are designed to work seamlessly with each other, in whichever combination suits the needs of the user."
Add styling
Here’s our design showing the spacing tokens that we need to add. We also need to set the type style and borders.
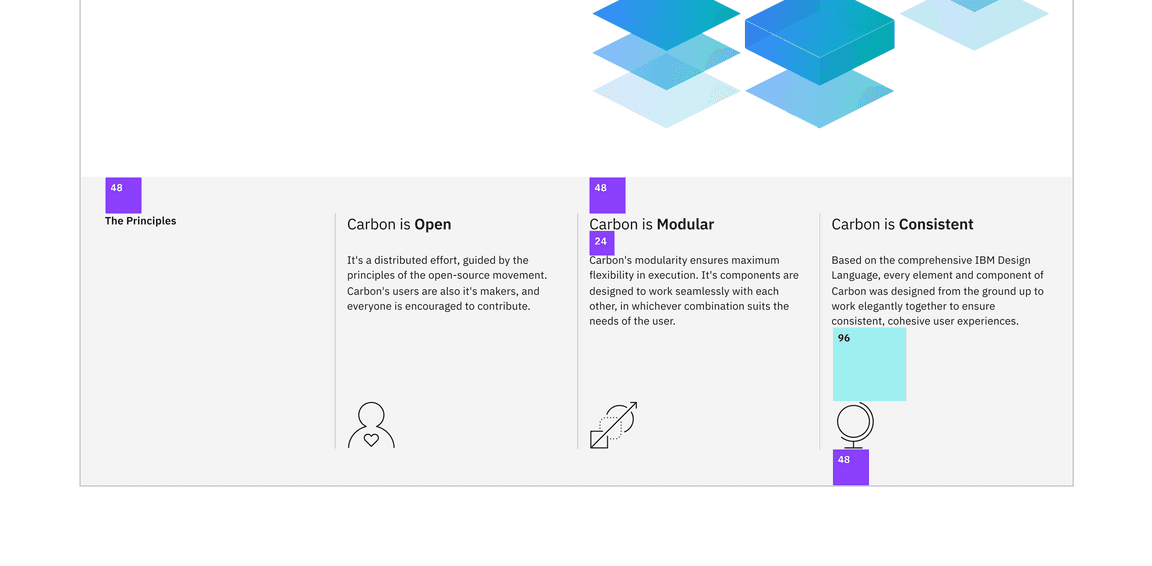
Info section spacing
Layout
Starting with layout, add the style section to
src/components/InfoSection/InfoCard.vue
<style lang="scss">@import "../../styles/carbon-utils";.info-card {margin-top: $spacing-09;display: flex;flex-direction: column;svg {
Once you save, go ahead and resize your browser to see the responsive layout at the different breakpoints. Make sure to review these color and spacing tokens. There are also a few breakpoint mixins that may be new to you.
Type
Our
InfoCard
.info-card__heading {@include type-style('productive-heading-03');}
Also, the design has the last word in each subheading as bold. To accomplish that, add this computed property to
InfoCard.vue
computed: {// Take in a phrase and separate the third word in an arraysplitHeading() {const splitHeading = this.heading.split(" ");const finalWord = splitHeading.pop();return [splitHeading.join(" "), finalWord];}}
Then, update
InfoCard.vue
splitHeading
Replacing
<h4 class="info-card__heading">{{heading}}</h4>
with
<h4 class="info-card__heading">{{ splitHeading[0] }}<strong>{{ splitHeading[1] }}</strong></h4>
Finally, add the following declaration block in the style section of
InfoCard.vue
.info-card__body {margin-top: $spacing-06;flex-grow: 1; // fill space so icons are bottom aligned@include type-style('body-long-01');// prevent large line lengths between small and medium viewports@include breakpoint-between(321px, md) {max-width: 75%;}
Check accessibility
We’ve added new markup and styles, so it’s a good practice to check DAP and make sure our rendered markup is on the right track for accessibility.
With the browser extension installed, Chrome in this example, open Dev Tools and run DAP.

DAP violations
That first violation is for the off-screen “skip to content” link. This link isn’t shown and is used to assist screen reading, so the color contrast violation can be ignored.
But, those three other violations came from the
<article>
InfoCard
<article>
<div>
In
InfoCard.vue
<article>
<div>
Also it’s time to fix it if you didn’t but I’m sure you can manage that by yourself.
Submit pull request
We’re going to submit a pull request to verify completion of this tutorial step.
Continuous integration (CI) check
Run the CI check to make sure we’re all set to submit a pull request.
yarn ci-check
Git commit and push
Before we can create a pull request, stage and commit all of your changes:
git add --all && git commit -m "feat(tutorial): complete step 4"
Then, push to your repository:
git push origin vue-step-4
Pull request (PR)
Finally, visit carbon-tutorial to “Compare & pull request”. In doing so, make sure that you are comparing to
vue-step-4
base: vue-step-4